In recent years, China has placed significant emphasis on enhancing its prowess in sports, both domestically and on the international stage. This initiative, commonly referred to as the "体育强国战略" (Tǐyù qiángguó zhànlüè) or "Sports Strong Nation Strategy," encapsulates the nation's multifaceted approach to becoming a global leader in athletics. Let's delve into the components and implications of this strategy.
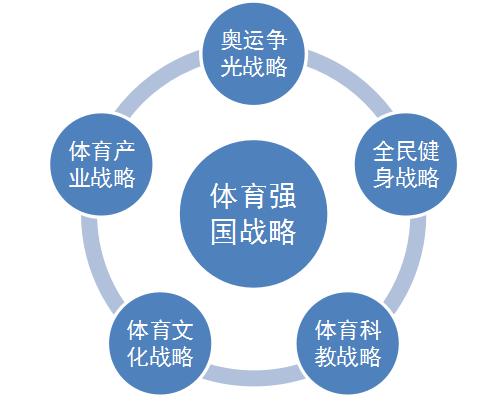
The Sports Strong Nation Strategy was introduced as part of China's broader national development agenda, aiming to bolster the country's athletic achievements and infrastructure. It reflects the recognition of the integral role sports play in national pride, soft power projection, and overall societal wellbeing.
1. Infrastructure Development: China is investing heavily in constructing stateoftheart sports facilities, including stadiums, training centers, and Olympic parks. These facilities not only provide athletes with worldclass training environments but also serve as venues for hosting international sporting events.
2. Grassroots Participation: The strategy emphasizes increasing participation in sports at the grassroots level, particularly among youth. Schools and community organizations are encouraged to promote physical education and extracurricular sports activities to nurture talent from a young age.
3. HighPerformance Training: Elite athletes receive extensive support through specialized training programs, sports science research, and access to cuttingedge technology. This focus on highperformance training aims to cultivate worldclass athletes capable of competing at the highest levels of international competition.
4. International Cooperation: China actively engages in international sports exchanges, collaborations, and competitions to enhance its global competitiveness. Partnerships with other nations, sports federations, and organizations facilitate knowledge sharing, talent exchange, and cultural diplomacy.
The implementation of the Sports Strong Nation Strategy carries several implications and benefits:
National Pride: Success in sports fosters a sense of national pride and unity among Chinese citizens, bolstering social cohesion and patriotism.
Soft Power: Sporting achievements enhance China's soft power on the global stage, shaping international perceptions and influencing diplomatic relations.
Health and Wellbeing: Promoting sports participation contributes to improved public health and wellbeing by encouraging physical activity and healthy lifestyles.
Economic Growth: The sports industry generates revenue through ticket sales, broadcasting rights, sponsorship deals, and tourism, contributing to economic growth and job creation.
Despite its ambitious goals, the Sports Strong Nation Strategy faces several challenges and considerations:
Resource Allocation: Balancing investments in sports infrastructure, athlete development, and grassroots programs requires careful resource allocation and longterm planning.
Competition: Achieving dominance in certain sports disciplines requires surpassing fierce competition from established sporting powerhouses.
Social Equity: Ensuring equal access to sports opportunities and resources across diverse socioeconomic backgrounds is essential to promote inclusivity and fairness.
China's Sports Strong Nation Strategy represents a comprehensive effort to elevate the country's standing in the global sports arena. By prioritizing infrastructure development, grassroots participation, highperformance training, and international cooperation, China aims to realize its vision of becoming a sporting powerhouse while reaping the associated benefits for its society, economy, and international stature.